An abrasive wheel is a disposable tool made from an abrasive material or compound. These wheels are typically found on grinders, grinding machines, and metal cut-off saws. Abrasive wheels are a very versatile tool. They rotate at high speed and are capable of of cutting, shaping, smoothing and cleaning a wide variety of materials. So, engineers, builders, bricklayers, electricians, carpenters, fitters and welders widely use them at work.
However, since the the abrasive wheels rotate at high speed, they are capable of causing severe injuries. According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), almost half of all accidents that involve an abrasive wheel occur due to operator error or an unsafe work system. So, anyone whose work involves using or handling abrasive wheels, must be aware and follow strict health and safety practices to protect both themselves and anyone around them.
Through our knowledgeable manufacturing sector courses, we wanted to use this article to educate you on the safe use of abrasive wheels.
Common machines associated with abrasive wheels
You are most likely to come across abrasive wheels in bench grinders, pedestal grinders and portable grinders.
Bench grinders permanently stay on a bench top. They are used in workshops for sharpening tools, rough shaping and removing burrs.
Pedestal grinders have a mounted wheel that sits within a pedestal. They are used to work on extremely hard materials and sharpen cutting tools.
Portable grinders are hand-held power tools, such as angle grinders. They are used for grinding, cutting and polishing. Portable grinders are common in metalworking and construction sites, as well as in the emergency rescues.
Uses of abrasive wheels

There are many different types of abrasive wheels, making them suitable for a wide variety of different tasks. Some examples include:
Straight wheels are basic grinding wheels often used in home workshops. They can be found on bench or pedestal grinders. Straight wheels are most commonly used for surface grinding and to sharpen tools, such as wood chisels and lawnmower blades.
Cup wheels can re-sharpen, finish or polish concrete and stone. However, with a small enough grit they can also remove adhesive and paint from materials.
Dish wheels look similar to cup wheels but are shallow and have a thinner edge. Their shape allows the tool to reach into narrow cracks and crevices that a cup wheel cannot access.
Cut-off wheels usually have a very narrow grinding surface. They make deep, narrow, precise cuts at 90-degree angles. They are used with both portable and stationary tools on numerous materials including aluminium, plastic, sheet metal and stainless steel.
Segmented wheels have segmented sections instead of a continuous rim. When used with cooling or lubricating fluids, these wheels remove large amounts of material rapidly without damaging its surface.
Plug and cone wheels can clean and remove excess metal from castings where other wheels cannot easily access.
What are the dangers of abrasive wheels?

Incorrect use of abrasive wheels can cause devastating injuries and even death. Almost half of all accidents that involve an abrasive wheel happen due to operator error or an unsafe work system. So, operators must follow instructions and adhere to strict health and safety requirements to reduce the risks of injury. The dangers of abrasive wheels include:
1. Drawing-in and contact with the wheel
An abrasive wheel rotates at high speed and is capable of causing severe injuries if it comes into contact with any dangling items. For example, rags and waste can become entangled into the wheel when they come into contact, causing wheel breakage. Also, loose clothing, long hair or body parts can come into contact with the rotating wheel, may wrap around it and draw into the wheel. This can severely injure the operator.
2. Breakage and ejection of particles
Every wheel has the inherent risk of wheel breakage. If a wheel breaks while rotating at a high speed, it can eject particles at its rotation speed. This can cause serious wounds and can even be fatal.
3. Dust and flying particles
When cutting and grinding materials, dangerous dusts, smokes and flying particles can spread into the air. It can cause coughing, sneezing, asthma attacks and develop into serious respiratory issues in the long term. For example, when cutting concrete, brick or stone, silica dust can spread into the air. When a person inhales silica dust, the particles scar lung tissue and can cause silicosis – incurable lung disease.
4. Noise
Working with abrasive wheels can produce an incredibly loud noise. Both short or prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause tinnitus and permanent hearing loss.
5. Hand Arm Vibration (HAV)
Operating vibrating machinery can cause hand arm vibration syndrome. This condition can lead to damage to the nerves, joints and muscles.
6. Burns, fire and explosion
Grinding and cutting materials can cause sparks and start fire if the operator is carrying out work close to flammable materials.
7. Electric shock
There is a risk of electric shock if the operator cuts into cables or exposed live parts.
8. Exposure to hazardous substances
Grinding and cutting operations often involve the use of grinding fluids, lubricants and coolants. Workers are at risk of inhaling fluid mist and vapour, which can cause asthma, bronchitis, irritation of the respiratory tract and breathing difficulties. Also, the exposure may cause irritation to eyes, nose, throat and skin.
9. Working in confined spaces
Tight, confined spaces can have high dust and fume concentration, which can cause harm to the operator’s health. It also poses a high risk of fire.
How to prevent abrasive wheel injuries?

Most abrasive wheel injuries are due to operatives using the wrong type of wheel or using it in the wrong way or just not following the correct safety protocols.
Mainly these injuries are either caused by contact with the tool itself or by materials ejected during operation. Common injuries include: Cuts to skin, Finger amputation, Eye injuries, Head injuries and Foot injuries.
You can prevent most accidents that occur with abrasive wheels by ensuring, thorough training is delivered to operatives, appropriate PPE is always worn and by following the guidelines below.
To ensure you keep safe whilst using abrasive wheels, you should:
- Read and understand supplier’s safety instructions.
- Ensure the wheel is suitable for the task.
- Check the safety guard is in place before use.
- Ensure work rests are properly adjusted.
- Only mount compatible abrasive wheels.
- Wear suitable clothing.
- Wear PPE to protect you from the risk of projectiles and dust inhalation.
- Always change wheels when they become worn.
- Always check the work area before using an angle grinder, and remove or protect any combustible or flammable materials.
- Visually check the tool before use, have periodic portable appliance testing.
Abrasive wheel markings
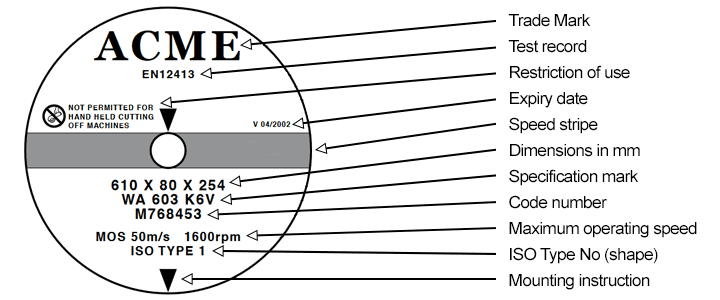
Abrasive wheels have specific markings that help users to select the correct wheel for the equipment and task they need to carry out. Knowing which wheel to use for each task and type of machinery is a vital skill. Using the incorrect wheel for a task can have serious consequences. There is a British standard for marking abrasive wheels.The wheel markings must follow Annex A of BS EN 12413 and BS ISO 5255. Abrasive wheel markings must include the following information:
Trade mark – the wheel must have the manufacturer trade mark or brand.
Test record – it indicates that the wheel meets the required safety standards.
Restrictions – the label may include accompanying information for restrictions on use and will indicate if the wheel is suitable for a task. Also, the wheel markings may indicate PPE requirements and other safety precautions.
Expiry date – wheels have a marking of the expiry date. Operators should never use an abrasive wheel after the expiry date.
Dimensions – the wheel label provides wheel’s diameter, thickness and hole size in millimetres.
Specification mark – it provides information on the composition and structure of the wheel. It indicates the abrasive material, grain size and bond.
Manufacturer’s code – this is a traceable number that indicates the source and manufacturing details of the wheel.
Maximum speed – all wheels over 80mm in diameter should have a marking of maximum permissible speed on the label. The users must never exceed the maximum permissible speed of the wheel.
High speed wheels (50 m/s or more) have a colour-coded stripe in the centre of the wheel that indicate the maximum operating speed.
Additional information on markings can be found within HSG17 on the HSE website.
Abrasive wheels regulations
Employers must ensure employee’s health and safety at work. The following regulations determine employers’ and employees’ legal duties that apply when using abrasive wheels at work.
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 (HASWA)
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974, also referred as HASWA, places a duty on employers or anyone who has control over a workplace to protect employees or anyone in the premises against health and safety risks. This includes the risks posed by the use of abrasive wheels at work.
The management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
The management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 reinforce the HASWA by placing duties on employers, employees, contractors, designers and their clients to assess the health and safety risks to third parties and to take appropriate measures to protect them.
The provision and use of work equipment 1998 (PUWER)
The Provision and use of work equipment 1998, also referred as PUWER, aims to keep workers safe while using equipment and machinery. PUWER requires employers to:
- Ensure that all machinery and equipment are suitable for its intended use.
- Ensure that machinery and equipment are safe for use, in efficient working order, properly maintained, inspected and tested.
- Fully inform and provide adequate instruction and training to anyone using, supervising or managing the use of work equipment.
- Follow any accompanying health and safety measures, such as protective devices and controls. These include guarding, emergency stop devices, clearly visible markings.
- Take measures to prevent or control the risks to people.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) at work regulations
PPE at work regulations oblige an employer to assess the risks and hazards in the workplace and provide suitable PPE to all workers. This includes employees, contractors, temporary workers and anyone else carrying out work in the workplace. The employer is also responsible for the maintenance, storage and replacement of the PPE.
Other important UK legislation
The Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) is relevant to the use of abrasive wheels as during cutting and grinding, hazardous substances such as dusts and fumes can spread into the air. You can learn more about COSHH here.
The Control of Noise at Work Regulations 2005 is relevant to work with abrasive wheels, because grinding and cutting machines produce loud noise that can permanently damage hearing. Therefore, employers must put hearing protection measures in place.
The Control of Vibration at Work Regulations 2005 apply to the use of abrasive wheels because it exposes workers to the health risks associated with the vibration from hand-held cutting and grinding machines.
The Supply of Machinery (Safety) Regulations 2008 require wheel manufacturers to take all precautions to reduce the risk of breakage and ensure that wheels meet required safety standards.
Need Abrasive Wheels training?
We offer the following RoSPA-assured and CPD-certified online Abrasive Wheels Training Course.
Have a question?
If you have a question or require more information on any of our training courses. Please contact our friendly support team on 0333 577 5016 or sales@i2comply.com.




